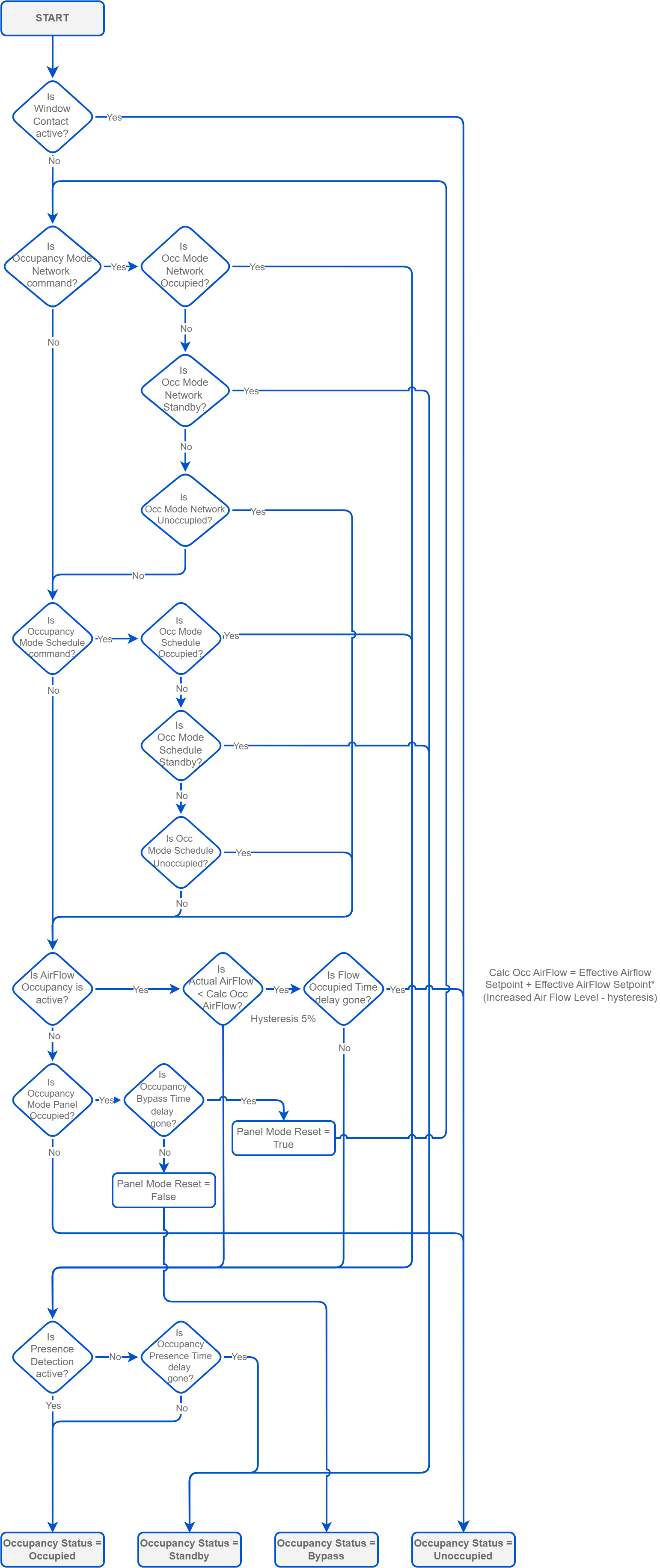
In the VAV application, occupancy is one of the factors determining the calculated airflow. In the application algorithm, the occupancy status has an impact on the control of a dead zone range to achieve maximum energy efficiency taking into account the user’s comfort temperature. The dead zone means that no cooling or heating is executed and the airflow is minimized. The algorithm is designed to adjust the dead zone to the occupancy status in order to maximize energy efficiency and minimize the effect on the user’s comfort – even the smallest range of the dead zone in the occupied mode generates savings for the system, while the effect on the user’s comfort is non-distinctive.
Primarily, the occupancy status is retrieved from the network. If there is no update from the network and the OccupancyMode Data Point falls into status different than OK, the local schedule is checked next and becomes a source for the occupancy status.
The occupancy status is also affected by the motion detector and window open/close state.
The motion detector, if available, is connected to the I1 digital input. Its state is read to the PresureSensor variable. The PresenceSensorInvert variable has two modes, normal and invert, which are used to control the sensor state interpretation. In the normal mode, if the value from I1 is true, it means the sensor has detected presence and the occupancy status is switched to occupied. If I1 is false, it means no motion has been detected. If the sensor does not detect motion after the StandbyTimeOverride time expires, it switches the status to standby (temporarily unoccupied). In the invert mode, if I1 is true, it means no presence has been detected, and if I1 is false, it means that motion has been detected.
Note
If there is no presence sensor connected, it is recommended to use the inverted mode, because in the inverted mode the constant state is motion detected.
The window contact switch is connected to the I2 digital input. Its open/close state is read to the WindowContact variable. The WindowContantInvert variable has two modes, normal and invert, which are used to control the sensor state interpretation. In the normal mode, if the value from the I2 is true, the window is open, if the value is false, the window is closed. In the invert mode, if the I2 value is true, it means the window is closed, and if the I2 is false, the window is open. Most contact switches work in the invert mode. If there is no contact switch installed on the window, the WindowContantInvert works in its default, normal, mode.
Occupied Mode
In the occupied mode, the application algorithm works to reach a desired comfort temperature taking into account the narrow dead zone (21-23°C/70-74°F) and provides the calculated airflow according to the following rules:
-
if the temperature rises above the dead zone range (>23°C/74°F), the algorithm increases the airflow;
-
if the temperature falls below the dead zone range (<21°C/70°F), the algorithm decreases the airflow.
Standby Mode (Temporarily Unoccupied)
The standby mode means that the area is temporarily unoccupied (e.g., an employee has left the room for a meeting). It is normally used in combination with the presence sensor. In the standby mode, the dead zone is expanded to the range of 19-25°C/67-77°F. The occupied status changes to standby after the time set in the StandbyTimeOverride variable (by default, 15 minutes). If the presence sensor detect motion again, the status changes back to occupied. Occupancy in the standby mode does not change automatically to unoccupied, only the signal form the BMS can trigger the unoccupied status (in the OccupancyMode variable).
Bypass Mode (Temporarily Occupied)
The bypass mode means that the area is temporarily occupied (e.g., in a spare conference room, which is normally unoccupied, the bypass mode would be used for an occasional meeting), the dead zone is the same as in the occupied mode (21-23°C/70-74°F) but it is active for a specific time (by default, 2 hours) and switches back to a previous state.
Unoccupied Mode
The unoccupied mode triggers the biggest range of the dead zone (16-28°C/64-80°F). The unoccupied mode is usually activated from the BMS or the local schedule.
Auto Occupancy
An additional option is the Auto Occupancy function which, when enabled in the AutoOccMode variable, examines the change in airflow in relation to the setpoint – when the measured value rises above 30% (the default value set in the OccupancyCalculator component, Increased Air Flow Level slot) the setpoint, the occupancy mode will switch to the Occupied state; when the measured value falls below 25% (by default, -5%) and maintains this difference for the Flow Occupied Time (by default, 5 min), it will return to the Unoccupied mode.