The article outlines how to integrate M-Bus meters in Niagara Workbench using the MbusNetwork driver and the M-Bus extension built-in the iSMA-B-MAC36NL-M or the MbusTcpIpNetwork driver with the iSMA-B-MG-IP gateway. The M-Bus configuration is not covered in this article; it has been covered in the M-Bus - configuration article. The meters discovery process is the same for both networks.
1. Devices Used for the Article
For this article the following devices have been used:
-
the iSMA-B-MAC36NL-M controller;
-
the iSMA-B-MG-IP module;
-
three M-Bus meters, configured as indicated in the table:
|
Primary Address |
Device ID (Serial Number) |
Manufacturer ID |
Medium (Device Media) |
Device Version |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
8 |
16210171 |
ACW |
Water |
14 |
|
2 |
15 |
00331533 |
APA |
Water |
21 |
|
3 |
36 |
20702297 |
BMT |
Water |
01 |
Table 1. List of M-Bus meters mentioned in the article
2. ‘Primary Address’ Discovering
The M-Bus protocol standard ensures that each meter has a unique ‘secondary address’. The ‘primary address’ is most often by default set to 1. In order to use the ‘Primary Address Search Discover’ feature, set the meters in the network with their own unique primary addresses. Then, in the Niagara Workbench, go to the Mbus Device Manager of the MbusNetwork or MbusTcpIpNetwork components, and select 'Discover'.
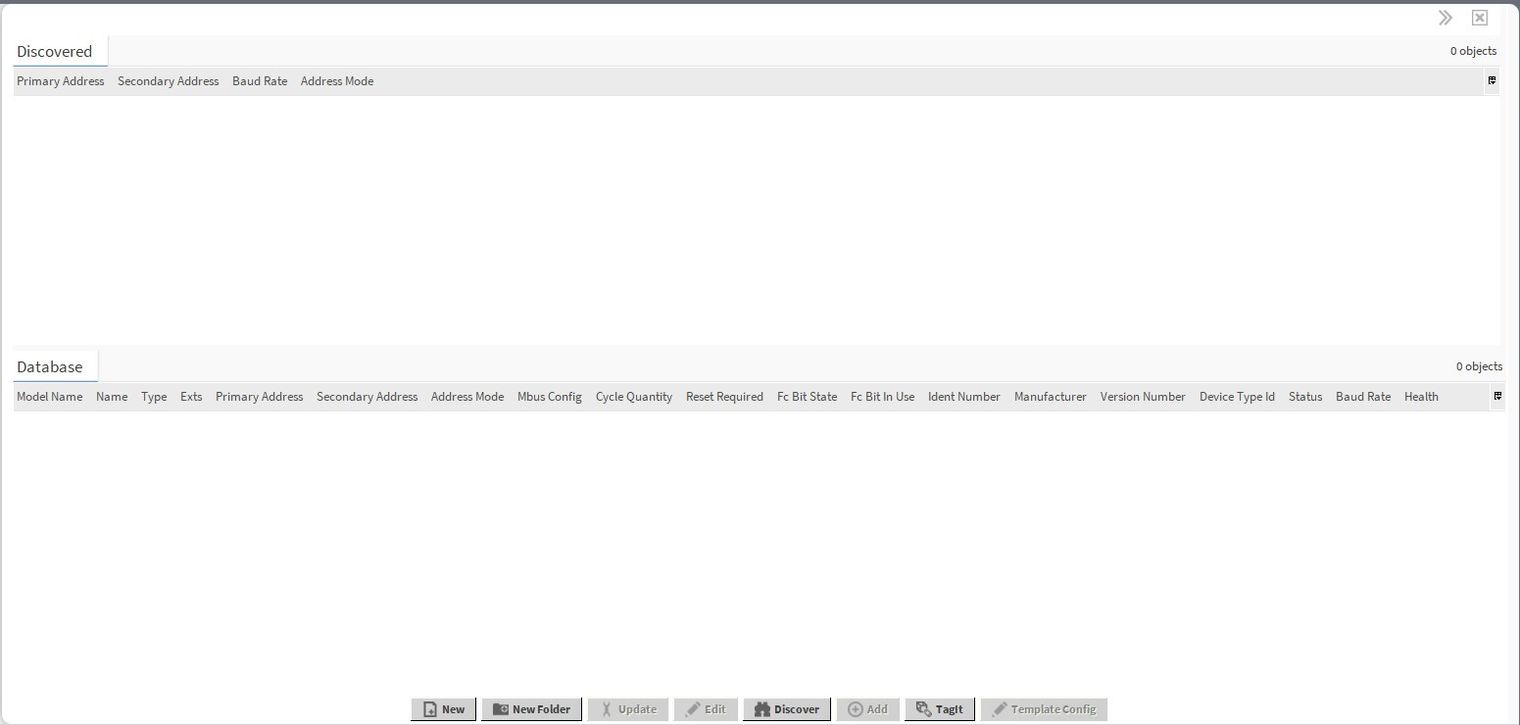
Figure 1. The Mbus Device Manager view with the Discover button
In the Discovery Wizard pop-up window, select the ‘Primary Address Search Discover’ option, and click Next. Then, select the meters' communication baud rate, and click Next.
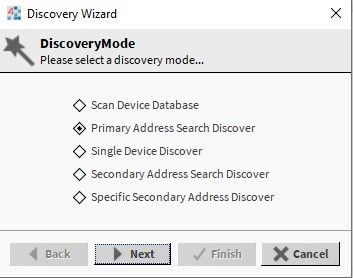
Figure 2. Meters discovering mode selection
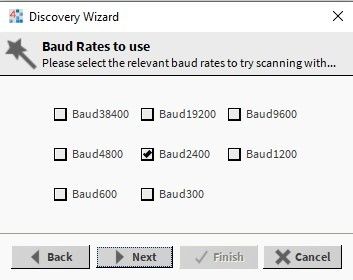
Figure 3. Communication baud rate selection
In the next window, it is possible to limit the addresses range to be discovered; it allows to significantly speed up the discovery process. In the last window, configure parameters such as: ‘Retry count’ (number of repeated requests), ‘Response timeout’ (time set to wait for the device’s response), ‘Inter message delay’ (pause between consequent requests), ‘Initialization delay’ (time to initialize a slave device). Niagara offers two predefined configuration modes - ‘Mbus standard speed scan’ (standard discovery) and ‘Slow speed scan' (slow speed discovery). Additionally, the user can individually configure specific parameters with the ‘Customized timings based scan’. The settings need to be adjusted to the communication baud rate. With the 2400 baud rate, it is recommended to use the 'Mbus standard speed scan’ option.
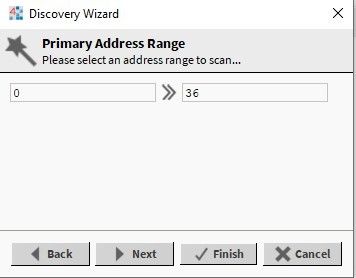
Figure 4. Limiting address range
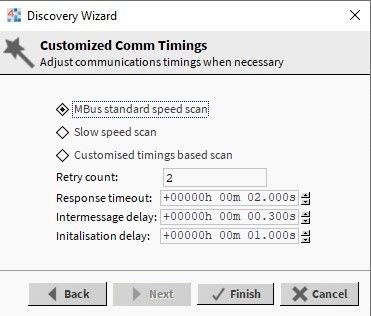
Figure 5. Discovery parameters configuration
Once the discovery configuration is completed, confirm it with the Finish button; the discovery process is started. Once the discovery process is completed, the M-Bus meters should be listed in the Discovered window. In the last step, drag&drop the meters to the Database window.
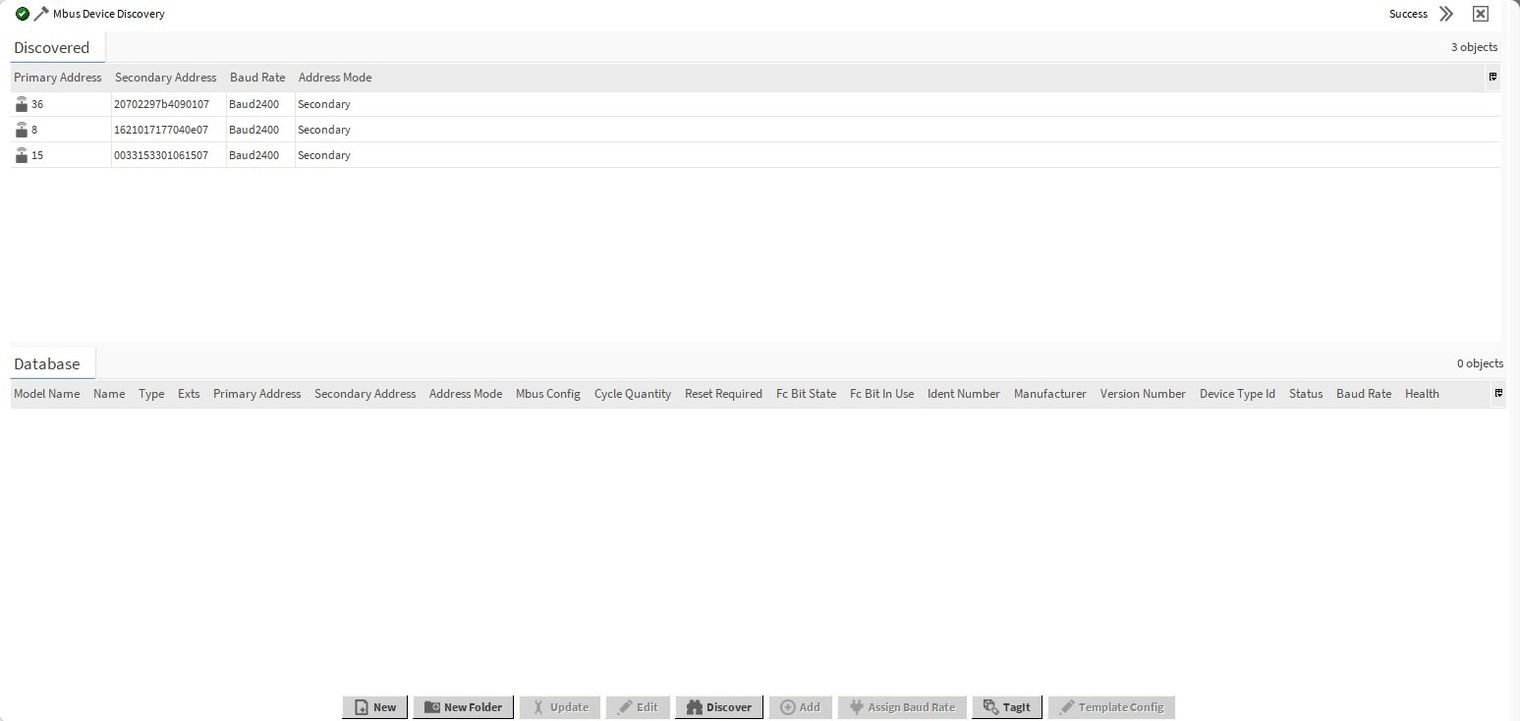
Figure 6. The Mbus Device Manager view with the discovered meters
WARNING! The ‘Baud Rates to use’ window appears only for the MbusNetwork driver. In case of the MbusTcpIpNetwork driver, the baud rate is configured in the M-Bus gateway settings.
2. Single Device Discovering
In the M-Bus network, if there are meters with the same ‘primary addresses’, which are not known, the discovery process can refer only to a single device. It requires disconnecting the rest of meters from the bus. In the pop-up window, select the ‘Single Device Discover’ option, which is much quicker than discovering a single device with the ‘Primary Address Search Discover’ option searching through the whole range of ‘primary addresses’.
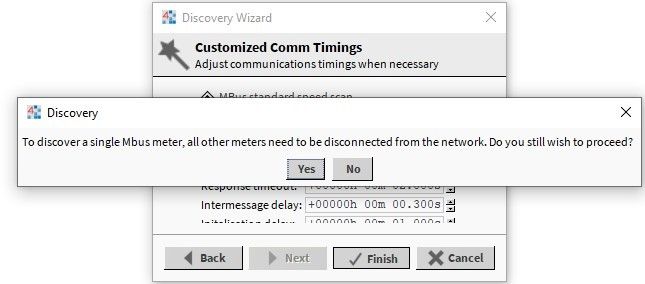
Figure 7. A warning telling to disconnect unnecessary meters from the bus
The discovery configuration process is the same as stated in section 1 of this article. Once the parameters are confirmed with the Finish button, the next pop-up window appears. Select Yes to confirm that there is only one M-Bus meter on the bus. When discovered and added to the station, change its ‘primary address’, and continue single discovering next meters.
3. ‘Secondary address’ Discovering
As mentioned above, the ‘secondary address’ is unique for each M-Bus device. It is defined by the following elements: ‘Device ID (Serial Number)’ 4 bytes, ‘Manufacturer ID' 2 bytes, ‘Medium (Device Media)’ 1 byte, ‘Device Version’ 1 byte. Niagara does not allow to discover a full range of the secondary addresses, therefore, the user has to know at least one of the secondary address elements, which allows to limit the discovered addresses range. Also, if the secondary address is limited by the ‘Medium’ parameter, the discovering is not processed properly in Niagara.
Therefore, the ‘secondary address’ discovering can be held threefold:
-
The ‘Specific Secondary Address Discover’ is limited by introducing the meter’s serial number to the ‘Secondary Address’ slot. Next, go through configuration steps according to section 1 of this article.
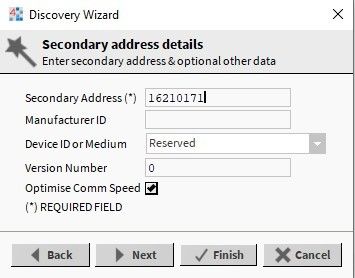
Figure 8. The ‘Specific Secondary Address Search’ with the meter’s serial number
WARNING! The ‘Specific Secondary Address Discover’ mode has to be selected in the DiscoveryMode pop-up window, appearing immediately after clicking the Discover button. Scenarios described below are available if the ‘Secondary Address Search Discover’ option is selected in the DisoveryMode pop-up window.
-
Limiting the range with the ‘Manufacturer ID’ parameter. Once the ‘Secondary Address Search Discover’ option has been selected, in the Filters window introduce the ‘Manufacturer ID’ of the meter, and then go through configuration steps according to section 1 of this article.

Figure 9. The Filters window with the meter’s ‘Manufacturer ID’
-
Limiting the range with the ‘Version Number’ parameter. Once the ‘Secondary Address Search Discover’ option has been selected, in the Filters window introduce the ‘Version Number’ of the meter, and then go through configuration steps according to section 1 of this article.
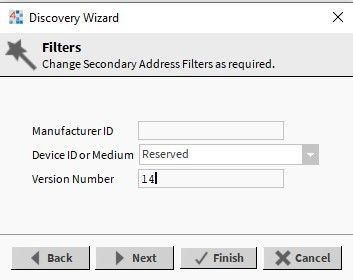
Figure 10. The Filters window with the meter’s ‘Version Number’
Introducing the ‘Manufacturer ID’ and ‘Version Number’ parameters together makes the discovering process even faster.
