The nano EDGE ENGINE SDK is designed to create user-customized libraries with components, which can be implemented directly in the iC Tool’s Software Manager and used in applications. The components' functionality may be enhanced by extensions, which can also be created with SDK.
In a nutshell, the nano EDGE ENGINE structure has 3 levels:
-
container (Applications, Networks, Services, and System);
-
components (such as Application in the Applications container);
-
components with or without extensions (basic control blocks).
-
-
The nano EDGE ENGINE SDK allows the user to create the last level of components, the basic control blocks, which can be located in the Applications or Services containers.
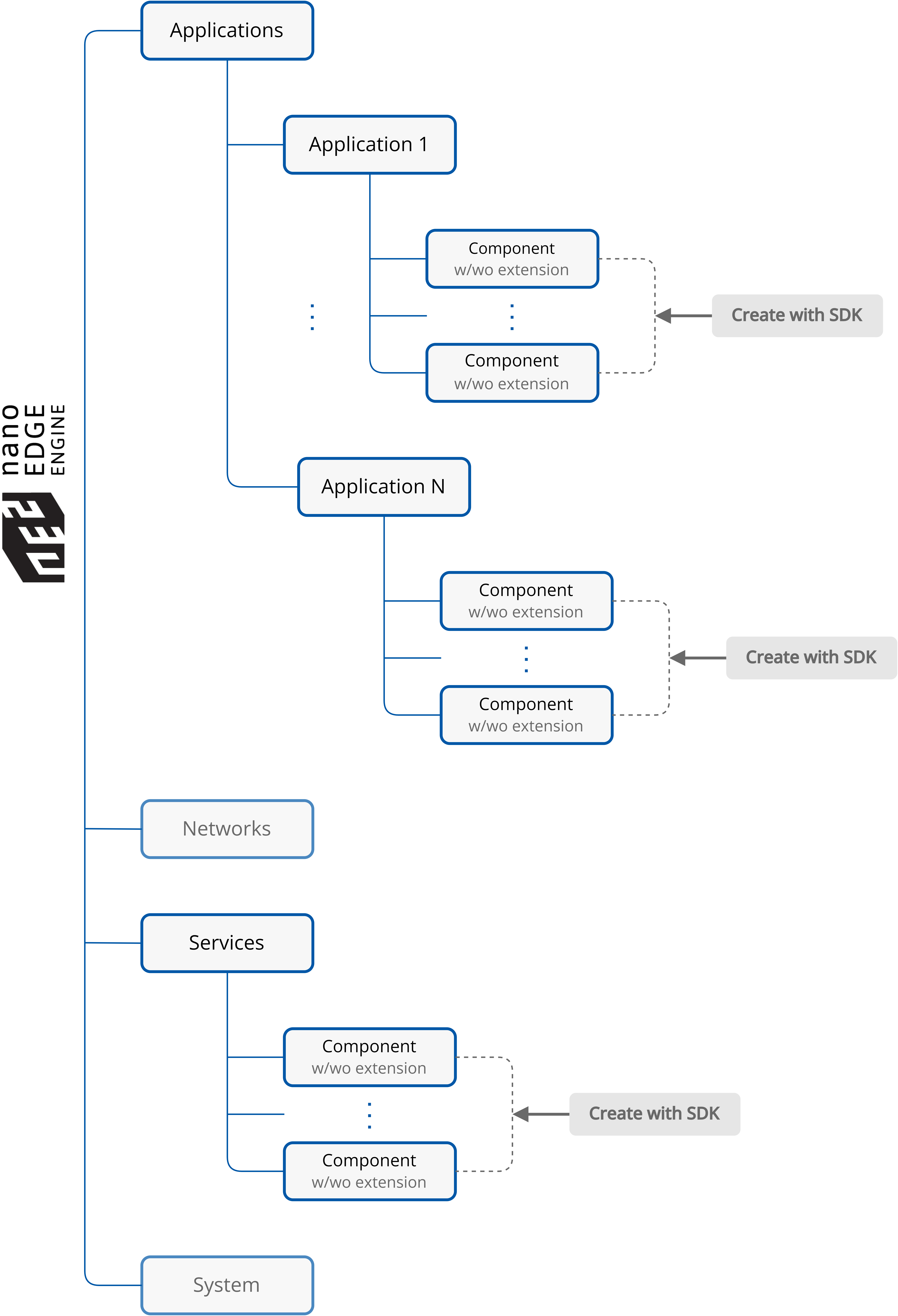
What are the Applications and Services containers?
Applications–a functional center of the device. Here are located Application components, which are designed to build user applications by adding components and linking them into a logical and mathematical sequences. Applications built with the nano EDGE ENGINE are cycle-driven, meaning the included components are executed in repeated periods of time lasting as long as a cycle time is set by the user—thanks to the efficiency of the nano EDGE ENGINE, the cycle may be as short as 100 ms (depending on the complexity of application), allowing effectively real-time calculations. The nano EDGE ENGINE allows constructing numerous independent, cycle-driven user applications that may work simultaneously. With the nano EDGE ENGINE the user may freely add as many Application components to the Applications container as needed. The only considerations here are the number of available licensed Data Points, available memory, or cycle time. Data Points are main application components, representing values in applications and allowing to connect services from the Networks container with the application—while connecting components from the Applications and Networks containers, it is recommended to use the Reference linking method. Data Points may be exposed to external networks, which means that external exposition of data from the Applications container or any other space may be carried out only via the Data Point.
Services—a utility center of the device. This container incorporates all services that enhance the basic functionality of the device. As the crude automation data transmission in the nano EDGE ENGINE is covered by services in the Networks container, the Services container provides the value added: these services cover an exchange of information with systems or devices superior to the building automation level. They may feed the algorithms with data that are normally unavailable in the building automation system, for example, a Weather service, which delivers information (precipitation, humidity, cloudiness, etc.) to the algorithm in the application managing garden watering, or an Alarm service, which sends out alarm messages to external recipients, provided certain limit values are exceeded. These services provide the additional logical layer to algorithms working within applications. They introduce external factors to user applications, enhancing their functionalities outside the core building automation. They may also introduce limit values to evoke certain actions in applications.
Find out more about the nano EDGE ENGINE structure: Basic concept of the nano EDGE ENGINE
Definitions
Library
The nano EDGE ENGINE library is essentially a folder that contains components. The library created with the nano EDGE ENGINE SDK is user-customized and can be implemented directly into the iC Tool’s Software Manager.
Naming recommendations
In theory, libraries created with the nano EDGE ENGINE SDK can be freely named, however, it is strongly recommended to maintain an original naming structure:
Library.Name-1.0.0000.00000.pe
The first part of a naming structure is Library.Name, where “Library” is a constant, and “Name”, coming after a dot (.), is a freely definable part. The library name is separated with a hyphen (-) from a version number.
Please note that the .pe file extension is required for libraries created with the nano EDGE ENGINE SDK.
Component
The nano EDGE ENGINE component is a basic control block, which can be used as part of an application (Applications container) or a service (Services container). Components are linkable.
The component’s functionality can be enhanced by extensions.
Extension
The nano EDGE ENGINE component’s extension is an enhancement of the component’s functionality. By its nature, it is an optional function of a component, which can be switched on and off according to user requirements.
Extensions can be added only to components that have this possibility defined in their code. It is also possible to declare that multiple extensions of the same type can be added to the same component.
Methods
Create Components
Init()
[protected virtual void Init()]
Init is called, as name suggests, when the component is initialized. It can be used to set up the component before it starts executing.
Execute()
[protected virtual void Execute()]
If a component needs to do something dynamically, like recalculate the output based on inputs or poll data, it can be done using the Execute method.
A components Execute method will be called by its parent service with the service's set frequency. For example, for an Application component with scan time of 200 ms, then every 200 ms the component will go through all of its children in order and call Execute for each of them.
OnRemove()
[protected virtual void OnRemove()]
Called once when the component is removed from device. Can be used for cleanup, unplugging events, etc.
ParentService()
[public ServiceBase ParentService()]
Returns the parent component that the component belongs to.
Create Extensions
Extensions
[public Extension[] Extensions]
List of all extensions attached to component.
AddExtension(Extension newExtension)
[public bool AddExtension(Extension newExtension)]
Adds an extension to component.
RemoveExtension(Extension target)
[public bool RemoveExtension(Extension target)]
Removes the target extension.
RemoveExtension(ushort atIndex)
[public bool RemoveExtension(ushort atIndex)]
Removes the extension at the specified position in the list.
RemoveAllExtensions()
[public bool RemoveAllExtensions()]
Removes all extensions from component.
GetExtension(ushort atIndex)
[public Extension GetExtension(ushort atIndex)]
Returns extension at the specified index.
