About M-Bus
The M-Bus (Meter Bus) was developed to fill the need for a system for networking and remote reading of utility meters, for example, to measure a consumption of gas or water in the house. This bus fulfils special requirements of remotely powered or battery driven systems, including consumer utility meters. If interrogated, the meters deliver the data they have collected to a common master, for example, a DDC controller or a hand-held computer, connected at periodic intervals to read all utility meters of a building.
Topology and Cable
The M-Bus is a hierarchical system, with communication controlled by a master device (for example, the AAC20-M). The M-Bus consists of a master, a number of slaves (end-equipment meters) and a two-wire connecting cable. The slaves are connected in parallel to the transmission medium–the connecting cable.
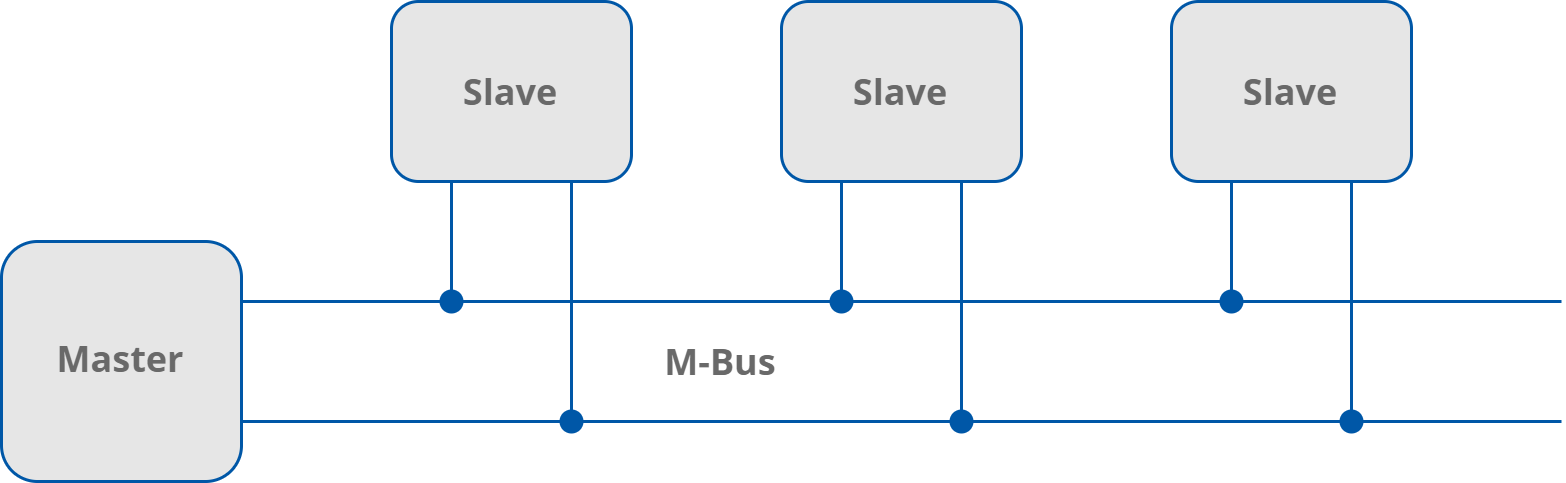
M-Bus connection topology
A two-wire cable (JYStY N*2*0.8 mm) is used as the transmission medium for the M-Bus. The maximum distance between the slave and the repeater is 350 m; this length corresponds to a cable resistance of up to 29 Ω. This distance applies for the standard configuration having baud rates between 300 and 9600, and maximum of 250 slaves. The maximum distance can be increased by limiting the baud rate and using fewer slaves, but the bus voltage in the space state must at no point fall below 12 V in a segment because of the remote powering of the slaves. In the standard configuration the total cable length should not exceed 1000 m in order to meet the requirement of a maximum cable capacitance of 180 nF.
M-Bus Addressing
M-Bus devices are using two types of addressing:
-
Primary: this address is assigned by a user in a commissioning process (all new M-Bus devices have this address, set by default to 0). This type of address has a limited range from 0 to 250;
-
Secondary: this address has a wider range than primary and, by default, contains a device serial number. All out-of-the-box devices connected to the bus have unique secondary address.
