The iC Tool has specially designed tabular drivers views to make the work of adding and maintaining the devices working in the network and exchanging data among them as easy as possible. Predefined drivers views will be discussed based on an exemplary complex configuration of many networks and devices.
Tabular drivers views may be divided into 3 hierarchical segments:
-
First segment is a table with the view of all drivers, that is networks. It is called Driver Manager. For example, the table shows the status of, among others, the following networks: localIO, ModbusAsync, OneWire, ModbusTCP, BACnet.
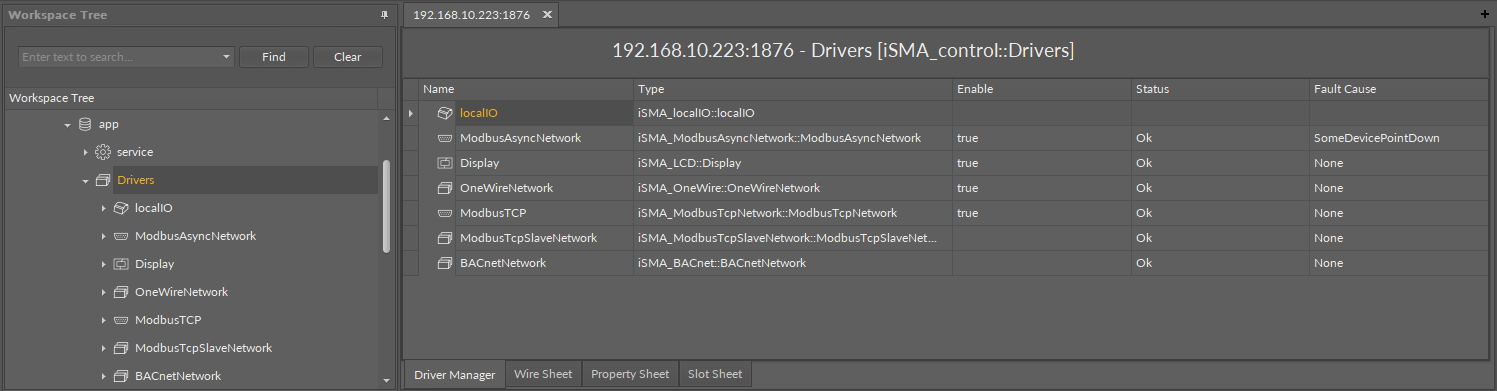
The first segment of tabular drivers views
-
Second segment shows the devices included in the network selected from the first segment. In the below example, the devices are ‘MIX18’ and ‘Mini4I4O’ for the network (driver)–ModbusTCP. The name of this view depends on the type of the chosen network, here it is the Modbus TCP Device Manager view.

The second segment of tabular drivers views
-
Third segment is a list of network points, which are variables allowing to read/record particular data from a particular device. In the below example, the digital points are RoomLight1-4, and they are read by the iSMA-B-4I4O device. The name of the views showing network points depends on the name of the device the data comes from, e.g., Modbus TCP Point Manager view.
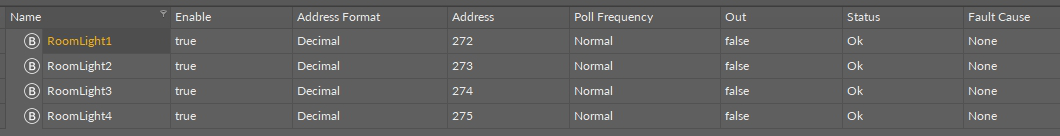
The third segment of tabular drivers views
Generally, the three drivers views’ segments described above may graphically be presented as follows:
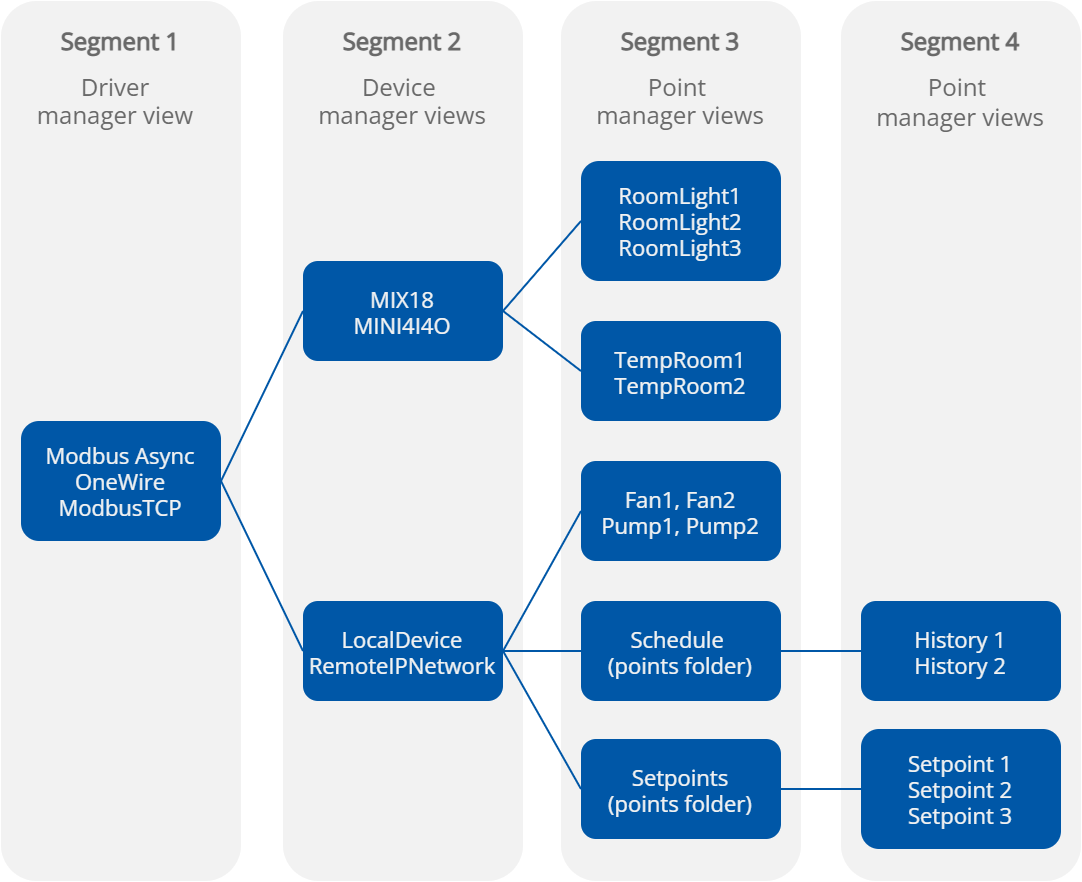
Driver views segments graphically
As depicted in the above diagram, network points may be grouped in network folders (Points Folder) and nested any number of times, which allows grouping and ordering large quantities of network points under a particular device (here, Schedule and Setpoints are folders grouping points History1,2 and Setpoint1,2,3, respectively).
The views construction of particular segments is very similar, so one type of table for each of the segments may display all the necessary data.
The next part focuses on how networks should be built based on devices distributed among Kits and points available in the iC Tool.
The further part focuses on how the XML configuration files are built and how the inbuilt tabular views for drivers views were defined. That knowledge may be used to build custom tabular views to expand drivers views with custom networks, devices, points, or to create completely new views for other application zones.
