Applicable to OS V1.7
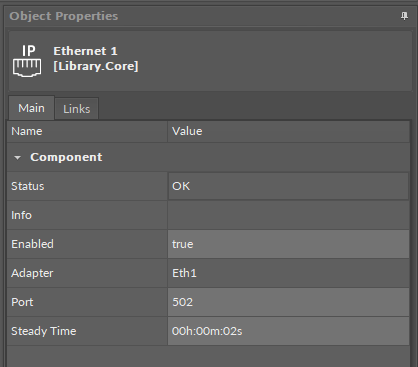
The Ethernet component allows to activate the BACnet IP or Modbus TCP/IP communication and to identify the port adapter and the number for the BACnet or Modbus network. The Ethernet component allows to identify the IP port number for BACnet or Modbus communication (by default, it is 47808 for BACnet IP and 502 for Modbus TCP/IP). It can be changed to any number from the slot's range (0-65535).
The Ethernet component has the following slots:
-
Status: indicates the current status of the component. If the component works properly, its status is OK; the component's status becomes Disabled if its Enabled slot has been set to false.
-
Available information: Disabled, OK;
-
-
Info: provides a detailed information about non-OK statuses of the component;
-
Available information:
-
Incorrect placement - must be placed under Interfaces container (status Fault): occurs if the component is added anywhere outside the Interfaces folder under BACnet or Modbus;
-
Incorrect configuration (status Fault): occurs when a parameter is missing or wrongly configured (e.g., port number is wrong);
-
Could not reserve port - already in use (status Fault): occurs if the component’s configuration duplicates parameters of a port which is already in use;
-
Port disabled (status Disabled): the Enabled slot in the component is set to false;
-
Network protocol disabled (status Disabled): the Enabled slot in BACnet or Modbus component is set to false;
-
There is a problem with the network protocol (status Disabled): the BACnet or Modbus component is in a status other than OK or Disabled;
-
-
-
Enabled: change of the slot's value enables or disables the component.
-
Available settings: true (enabled), false (disabled).
-
Note: If the Enabled slot is in false (meaning the component is disabled), the Status slot becomes Disabled.
Note: Disabling the component switches off BACnet IP server and client and Modbus TCP/IP server functions, which means that the device is not visible as the BACnet device/Modbus point in the network, and, in case of the BACnet client configuration, the communication with server devices is switched off too.
-
Adapter: informs, which communication port is used to connect to the network.
-
Port: allows to set the number of the port used to communicate in the BACnet IP/Modbus TCP/IP protocol.
BACnet
Additionally, the following slots are available if the component is configured for BACnet:
-
Object Id: shows the BACnet object ID automatically assigned to the interface;
-
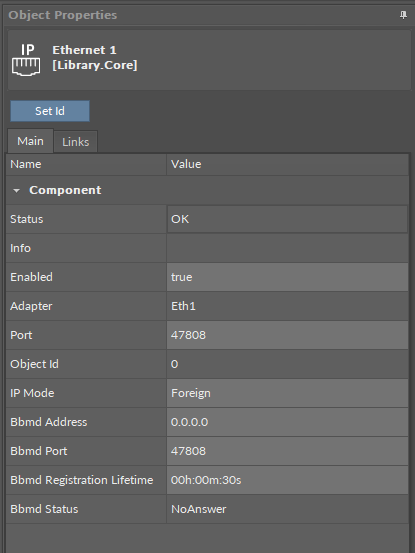
IP Mode: allows to select an operating mode for the IP port - normal of foreign (BBMD).
If the IP Mode slot is set to foreign, the following slots become available:
-
Bbmd Address: the IP address or DNS server of the BACnet Broadcast Management Device (BBMD) server; the default value is blank (0.0.0.0);
Note: If the BBMD IP address is left to its default value (0.0.0.0), registering to the BBMD server is disabled.
-
Bbmd Port: the UDP port of the remote BBMD server; the default UDP port value is 47808;
-
Bbmd Registration Lifetime: the number of seconds within which a foreign device must re-register with a BBMD; the default value is 30 s;
-
Bbmd Status: displays a BBMD server status.
What is BBMD?
The BACnet/IP Broadcast Management Device (BBMD) is a device added to the BACnet network, which broadcasts messages discovering devices on the network. The BBMD solution allows to overcome an issue of standard IP routers, which cannot forward BACnet messages for BACnet networks on multiple IP subnets (two or more). In such networks, each IP subnet, which is a part of a BACnet IP network with two or more subnets, needs a BBMD server in order to communicate.
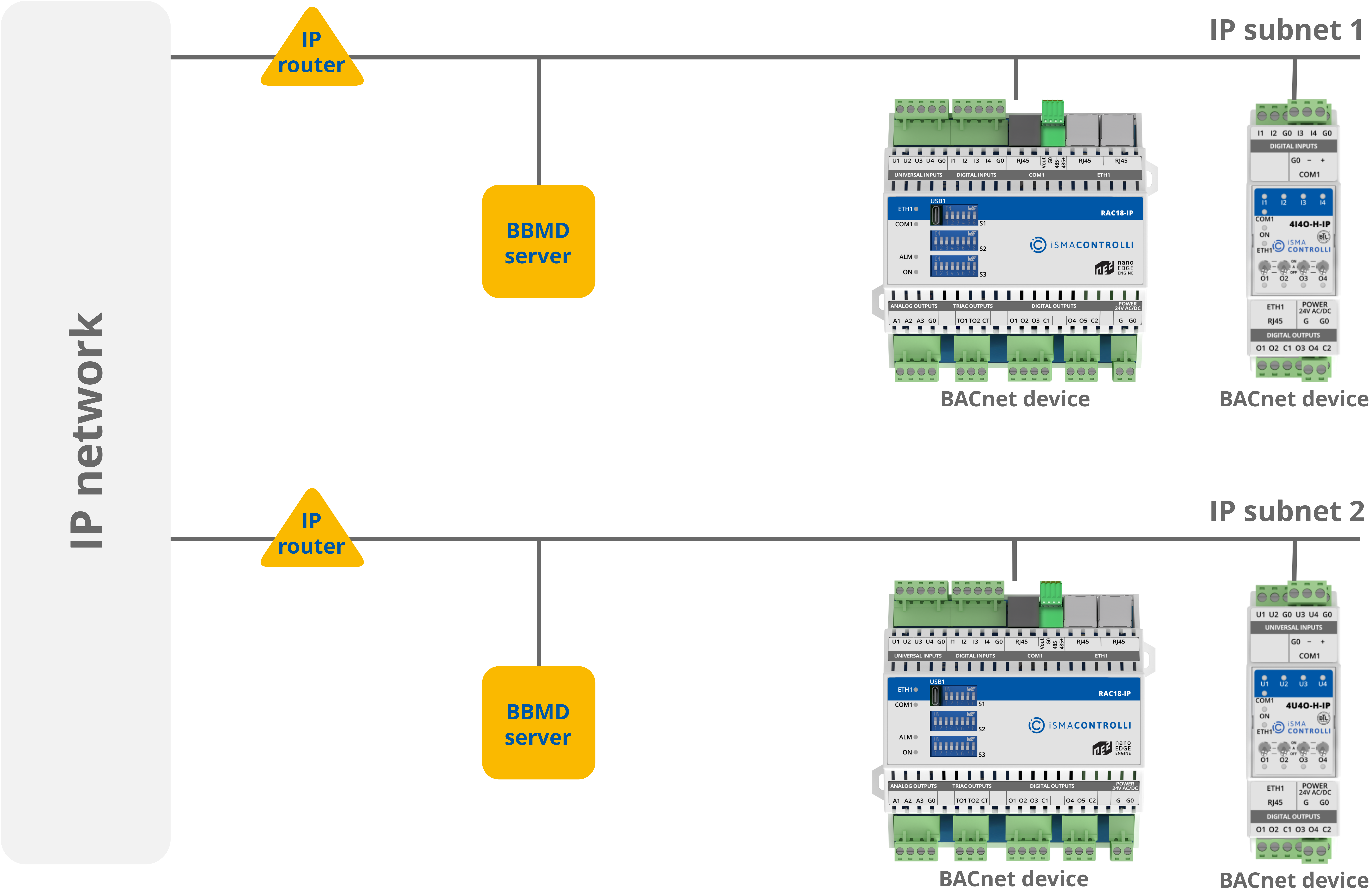
nano EDGE ENGINE Device as Foreign Device
The nano EDGE ENGINE device can be a foreign BACnet device. The foreign device is a BACnet device that has a different IP subnet address than those devices comprising the BACnet IP network, which the foreign device wants to join. The foreign device could be a full-time node on the foreign subnet or it could be a part-time participant. The foreign device mechanism is designed to enable communication with a BACnet IP network for BACnet devices, which present no economical sense to install, configure, or maintain a BBMD server for, or if there are no other BACnet nodes.
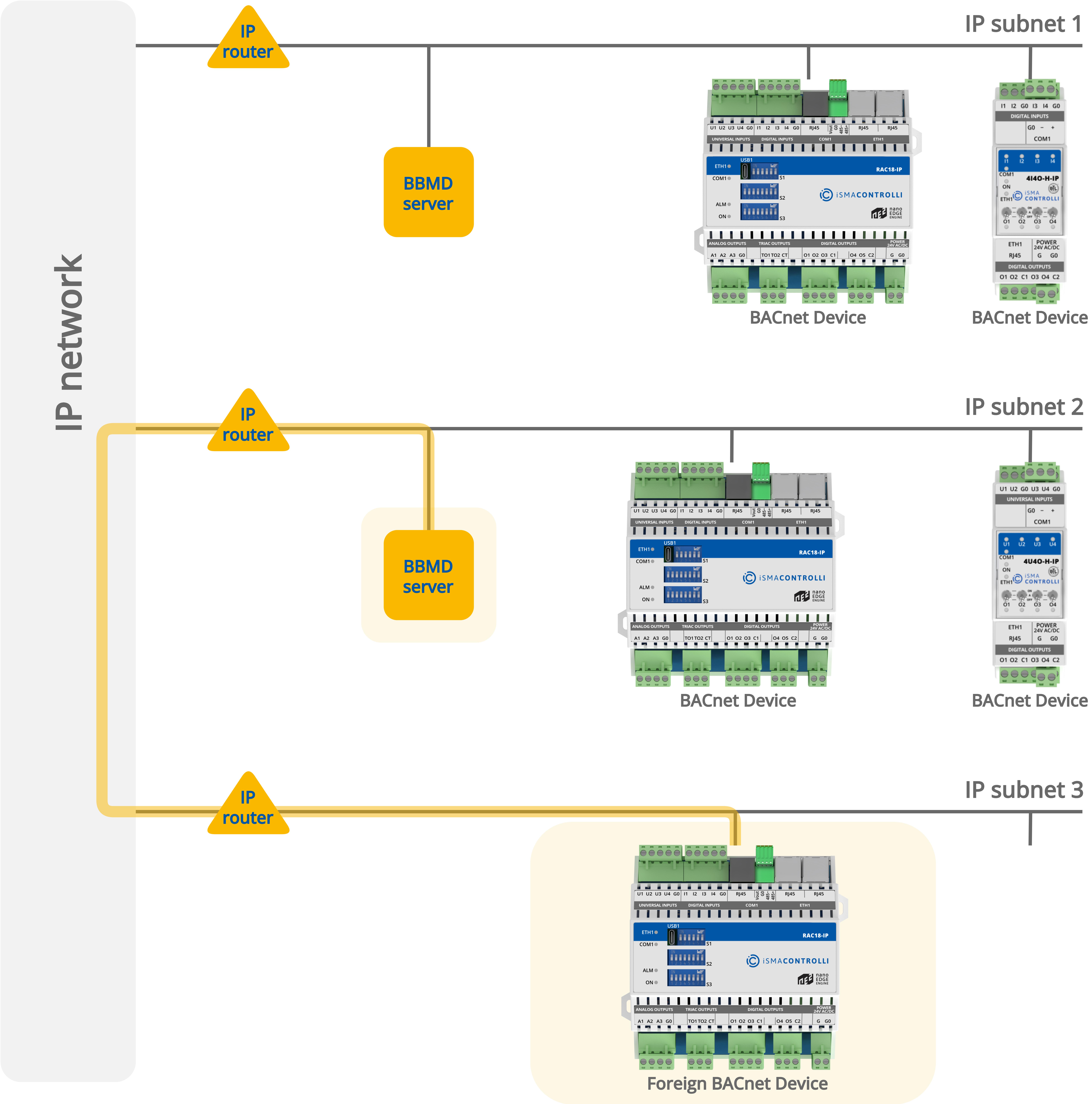
To register the controller as a foreign device, sending a request is necessary. The BBMD server address and port must be filled accordingly to the server configuration. Setting the foreign mode in the IP mode slot, automatically sends a request for the device to be registered to the BBMD server.
By registering with the BBMD server, the nano EDGE ENGINE device becomes a member of the BACnet IP network, and receives broadcast messages forwarded from the BBMD server, when they are available, and may request these messages be broadcast by the BBMD server on its behalf.
Once the message is received, the BBMD server adds the foreign device to its Foreign-Device-Table (FDT), and starts a timer equal to the BBMD Registration Lifetime. If the foreign device fails to re-register before the timer expires, the BBMD Server may delete the foreign device from its FDT.
Modbus
Whereas if the component is used in Modbus, the following slot is available:
-
Steady Time: allows to define the time from the start of the controller to the start of the communication on the Modbus client network.