This section provides a collection of procedures to use the iSMA-B-AAC20 Modbus drivers to build networks of devices with the Modbus points. The iSMA-B-AAC20 controller has one RS485 port, which can be used as a Modbus RTU/ASCII master.
The Modbus Async Network kit consists of 4 types of components:
-
Modbus Network;
-
Modbus Device;
-
Modbus Data Points;
-
Modbus Points folder.
Modbus Async License and Limitation
In the standard license there are available 500 data points, and this number cannot be expanded. The number of available points is shown in the ModbusAsyncNetwork component in the Free Points slot.
WARNING! Each device and data point is counted as one point. For example, to read 7 data points from 15 devices: Points number = 15 *(1 + 7) = 105.
Modbus Async Network Component
The ModbusAsyncNetwork is the main component, which is responsible for servicing the RS485 physical port. The component must be placed under the Drivers folder. The Modbus Network sets parameters such as communication baud rate and data format, testing, etc., and keeps statistics.
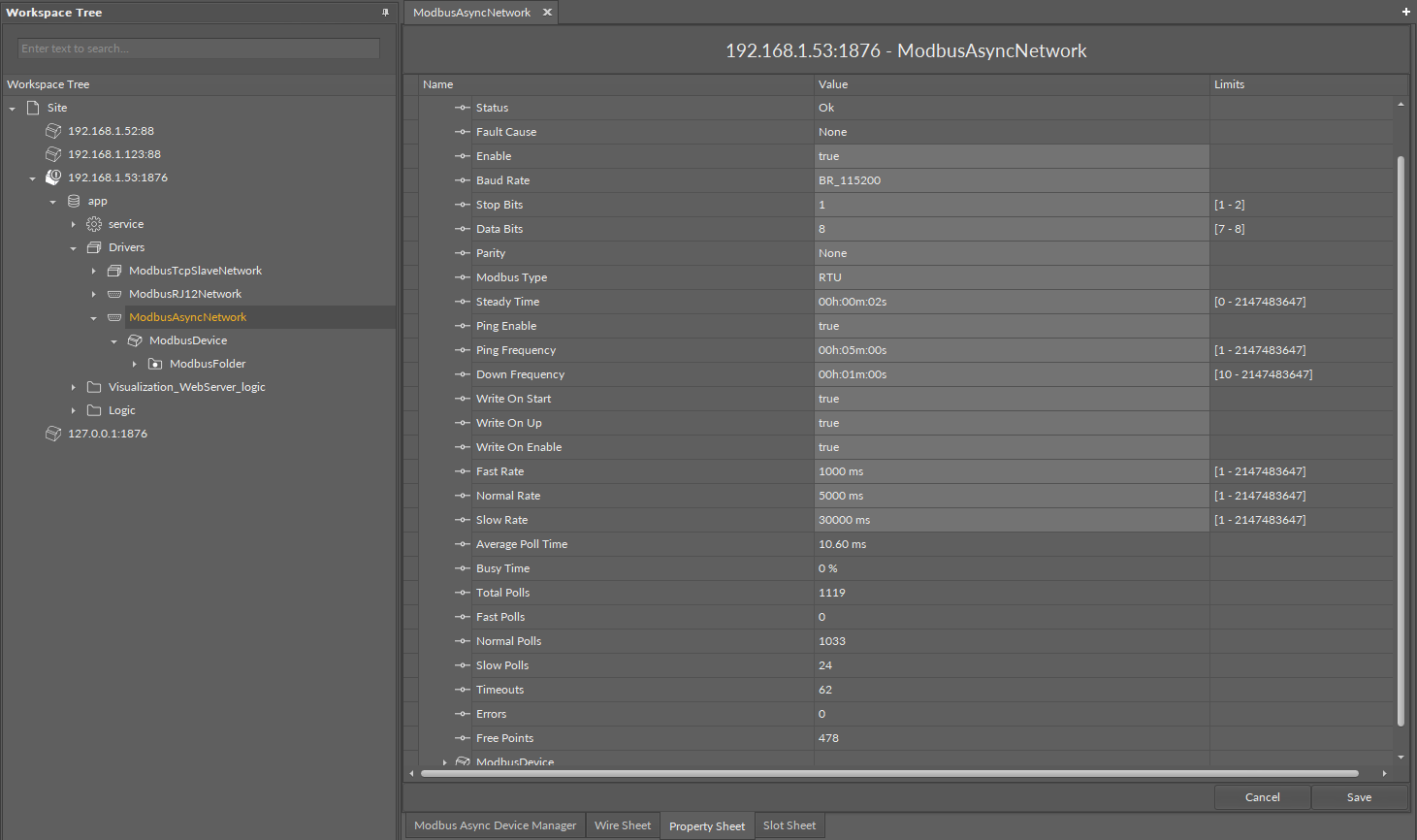
The ModbusAsyncNetwork component has the following slots:
-
Status: Network’s status;
-
Available states: OK (network is working properly), Disabled (network is disabled, the Enable slot is in false), OK some device/point down (error in the device or points);
-
-
Fault Cause: fault cause description;
-
Enable: this option switches on or switches off the Modbus Network;
-
true (network enabled), false (network disabled);
-
-
Steady Time: network start-up delay time after a power-up or reset;
-
Baud Rate: the Modbus RS485 port baud rate;
-
Available options: 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 bps;
-
-
Stop Bits: stop bit definition;
-
Available options: 1-bit, 2-bits;
-
-
Data Bits: data bits definition;
-
Available options: 7-bits or 8-bits;
-
-
Parity: parity bit definition;
-
Available options: None, Odd, Even, Always1, Always0;
-
-
Modbus Type: Modbus type definition;
-
Available options: RTU or ASCII;
-
-
Ping Enable: enables testing of the device’s connection;
-
Ping Frequency: time between testing messages to check the device’s connection;
-
Down Frequency: time between testing messages for devices or points, which have got the down status;
-
Write On Start: executes a write action in device writable components in the Modbus network after a reset or power-up;
-
Write On Up: executes a write action in device writable components in the Modbus network after restoring of the connection with Modbus device;
-
Write On Enable: executes a write action in device „Writable” components in the Modbus network after enabling the device;
-
Fast Rate: time between messages in the fast mode poll frequency;
-
Normal Rate: time between messages in the normal mode poll frequency;
-
Slow Rate: time between messages in the slow mode poll frequency;
-
Average Poll Time: average time for sending/receiving of one message;
-
Busy Time: percentage of Modbus network usage;
-
Total Polls: total number of messages;
-
Fast Polls: number of messages sent in the fast mode;
-
Normal Polls: number of messages sent in the normal mode;
-
Slow Polls: number of messages sent in the slow mode;
-
Timeouts: number of lost messages, the difference between sent and received messages;
-
Errors: number of error messages (for example, with the wrong CRC);
-
Free Points: number of available physical points in Modbus network.
The ModbusAsyncNetwork component has the following actions available under the right-click or in the Object Properties window:
-
Reset Stats: resets network’s statistics and starts counting from the beginning;
-
Enable/Disable: switching the Modbus network on/off.
